Low testosterone, also known as hypogonadism or low T, is a condition in which a man has a lower-than-normal level of testosterone, the primary male sex hormone. Testosterone is responsible for the development of male secondary sex characteristics, such as facial and body hair, a deeper voice, and muscle mass. It also plays a role in fertility and sexual function. Testosterone is pretty damn important, it needs to be monitored, regulated, and treated if necessary.

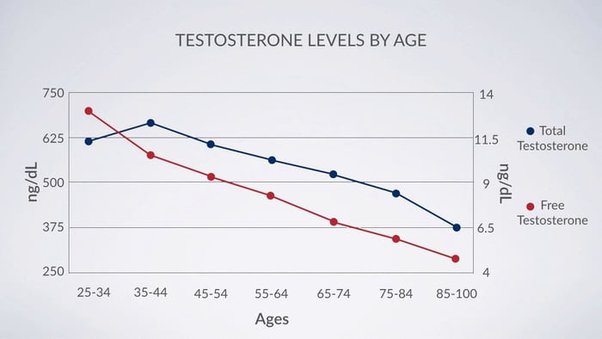
The prevalence of low testosterone varies by age, as testosterone levels naturally decline with age. It is estimated that about 2% of men under 40 years old and up to 50% of men over 80 years old have low testosterone. However, low testosterone can occur at any age and may be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Aging
- Chronic illness, such as diabetes or HIV/AIDS
- Certain medications, such as steroids or opiate painkillers
- Obesity
- Genetic conditions, such as Klinefelter syndrome
Symptoms of low testosterone in men
Symptoms of low testosterone may include:
- Low sex drive
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased muscle mass and strength
- Decreased bone density
- Fatigue
- Decreased body hair
- Enlarged breasts
To check for low testosterone, your healthcare provider may order a blood test to measure your testosterone levels. It is important to note that testosterone levels can vary throughout the day and may be affected by factors such as stress, illness, and certain medications. Therefore, it may be necessary to repeat the test on more than one occasion to get an accurate result.
Lifestyle factors related to low testosterone
Lack of sleep, poor diet, stress, and vitamin and mineral deficiencies can all contribute to low testosterone levels in men.
Lack of sleep: Testosterone levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day and are highest in the morning. Chronic sleep deprivation or poor sleep quality can disrupt the production and release of testosterone and other hormones, leading to low testosterone levels.
Poor diet: A diet that is high in saturated fat and sugar and low in protein, fruits, and vegetables may contribute to low testosterone levels. In particular, a deficiency in zinc, a mineral found in foods such as oysters, red meat, and beans, has been linked to low testosterone.
Stress: Chronic stress can affect the production and release of hormones, including testosterone. Stress may also lead to unhealthy behaviors, such as overeating and lack of physical activity, which can contribute to low testosterone levels.
Mineral and vitamin deficiencies linked to low testosterone
Vitamin and mineral deficiencies: Deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D and magnesium, may contribute to low testosterone levels.
It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, managing stress, and getting enough exercise, to support healthy testosterone levels and overall health. If you are concerned about low testosterone or other health issues, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and treatment. They can help identify any underlying causes and develop a plan to address them.
Treatment options for low testosterone
There are several treatment options for low testosterone, including:
- Testosterone replacement therapy: Testosterone replacement therapy involves taking testosterone in the form of injections, gels, patches, or pellets. This treatment is generally safe and effective at increasing testosterone levels and relieving symptoms of low testosterone.
- Supplements: Some supplements, such as DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone) or tribulus terrestris, are claimed to increase testosterone levels. However, the effectiveness of these supplements is not well-established and they may not be safe or suitable for everyone.
- Lifestyle changes: Making lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, exercising regularly, and reducing stress, may help improve testosterone levels and overall health.
FDA-approved treatments for low testosterone in men
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved several testosterone replacement therapies for the treatment of low testosterone in men. These include:
- Testosterone gel (AndroGel)
- Testosterone patch (Androderm)
- Testosterone injection (Depo-Testosterone)
- Testosterone implant (Testopel)
It is important to speak with a healthcare provider about the potential risks and benefits of testosterone replacement therapy and other treatment options for low testosterone. Your provider can help you determine the best course of treatment based on your individual needs and medical history.